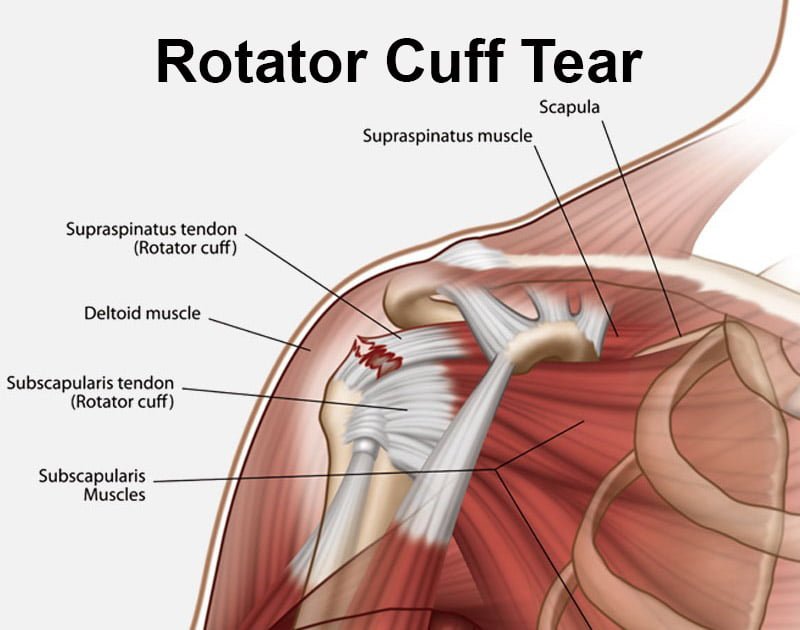
The rotator cuff is a group of muscles and tendons that surround the shoulder joint, providing stability and allowing for a wide range of motion in the shoulder. A tear in the rotator cuff can occur due to acute injury, such as a fall or lifting a heavy object, or it can develop gradually over time due to repetitive overhead movements or degenerative changes in the tendons.
Shoulder Rotator Cuff Tear
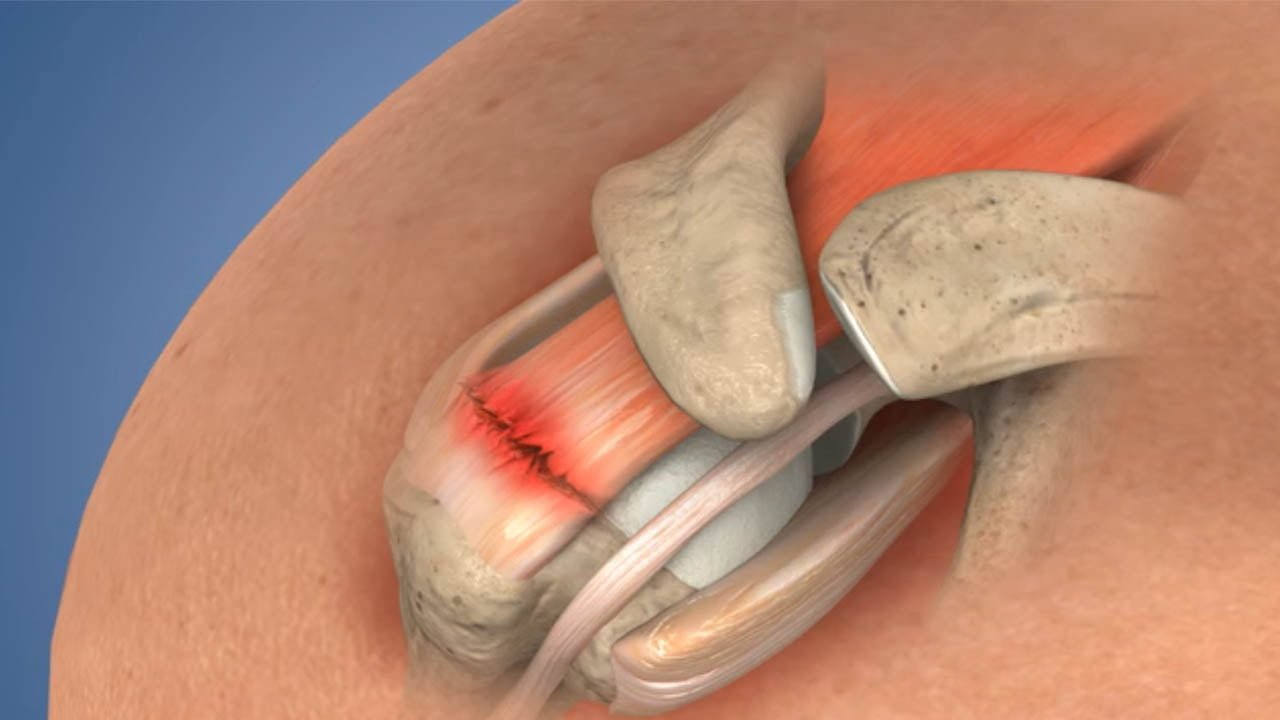
A rotator cuff tear is a common injury involving damage to one or more of the four muscles and tendons that stabilize the shoulder joint. This injury can result from sudden trauma or repetitive stress on the shoulder, leading to pain, weakness, and limited mobility.
A rotator cuff tear is a common injury that involves damage to one or more of the tendons in the shoulder joint, specifically those that make up the rotator cuff. The rotator cuff is a group of muscles and tendons that surround the shoulder joint, providing stability and allowing for a wide range of motion.
Symptoms of a rotator cuff tear may include:
- Shoulder pain, particularly when reaching overhead or behind the back.
- Weakness in the shoulder, especially when lifting or rotating the arm.
- Difficulty or pain when sleeping on the affected shoulder.
- Limited range of motion in the shoulder joint.
- Clicking or popping sensations with shoulder movement.
Diagnosis of a rotator cuff tear typically involves a physical examination by a healthcare provider, along with imaging tests such as an MRI or ultrasound to confirm the extent and location of the tear.
Following treatment, rehabilitation exercises are often prescribed to restore strength and range of motion to the shoulder. It’s crucial for individuals with a rotator cuff tear to follow their healthcare provider’s recommendations closely to optimize healing and prevent further injury.

FAQ...
What is a rotator cuff tear ?
A rotator cuff tear is a partial or complete tear in one or more of the muscles and tendons that make up the rotator cuff in the shoulder joint.
What are the causes of rotator cuff tears ?
Rotator cuff tears can be caused by acute trauma, such as a fall or lifting a heavy object, or by chronic overuse and degeneration of the tendon tissue over time.
What are the symptoms of a rotator cuff tear ?
Symptoms may include pain, weakness, and limited range of motion in the shoulder, particularly when lifting or reaching overhead, as well as pain that worsens at night or with certain movements.
How is a rotator cuff tear diagnosed ?
Diagnosis is typically based on a physical examination, medical history, and imaging tests such as X-rays, ultrasound, or MRI scans to assess the extent of the tear and rule out other potential shoulder problems.
What are the different types of rotator cuff tears ?
Rotator cuff tears can be classified based on their size (partial or full-thickness) and location (supraspinatus, infraspinatus, subscapularis, or teres minor tendon).
How is a rotator cuff tear treated ?
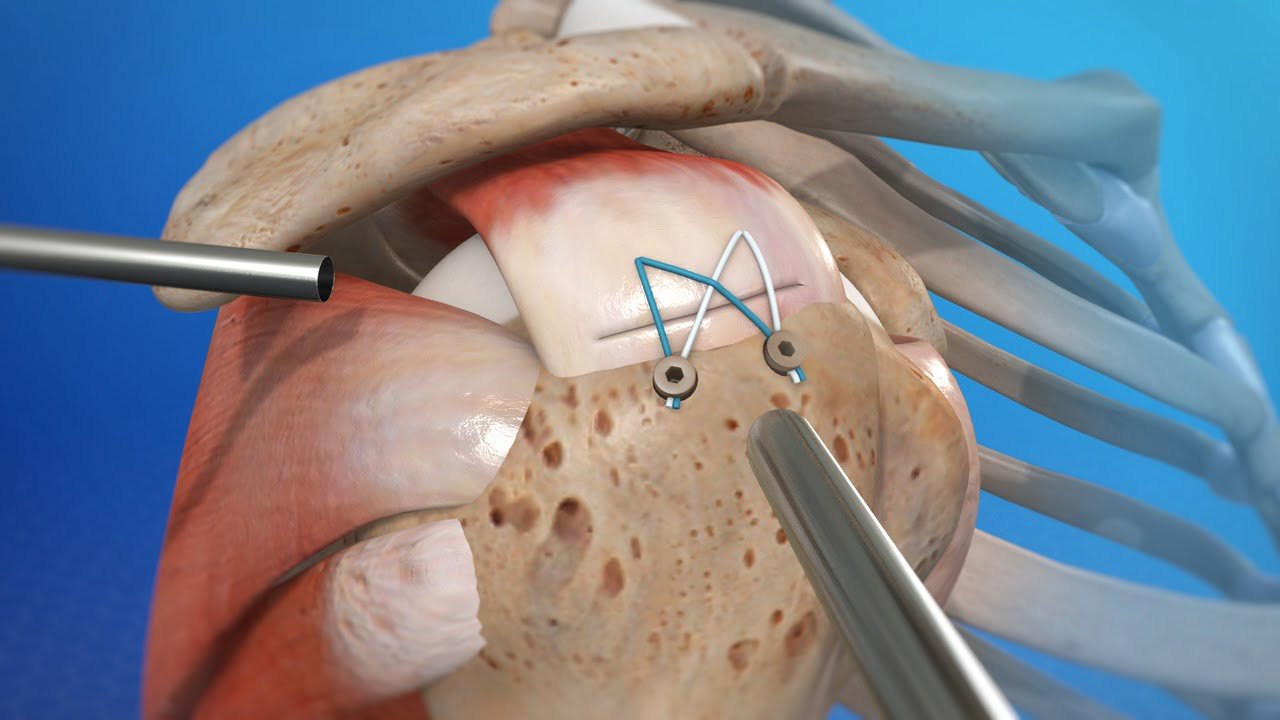
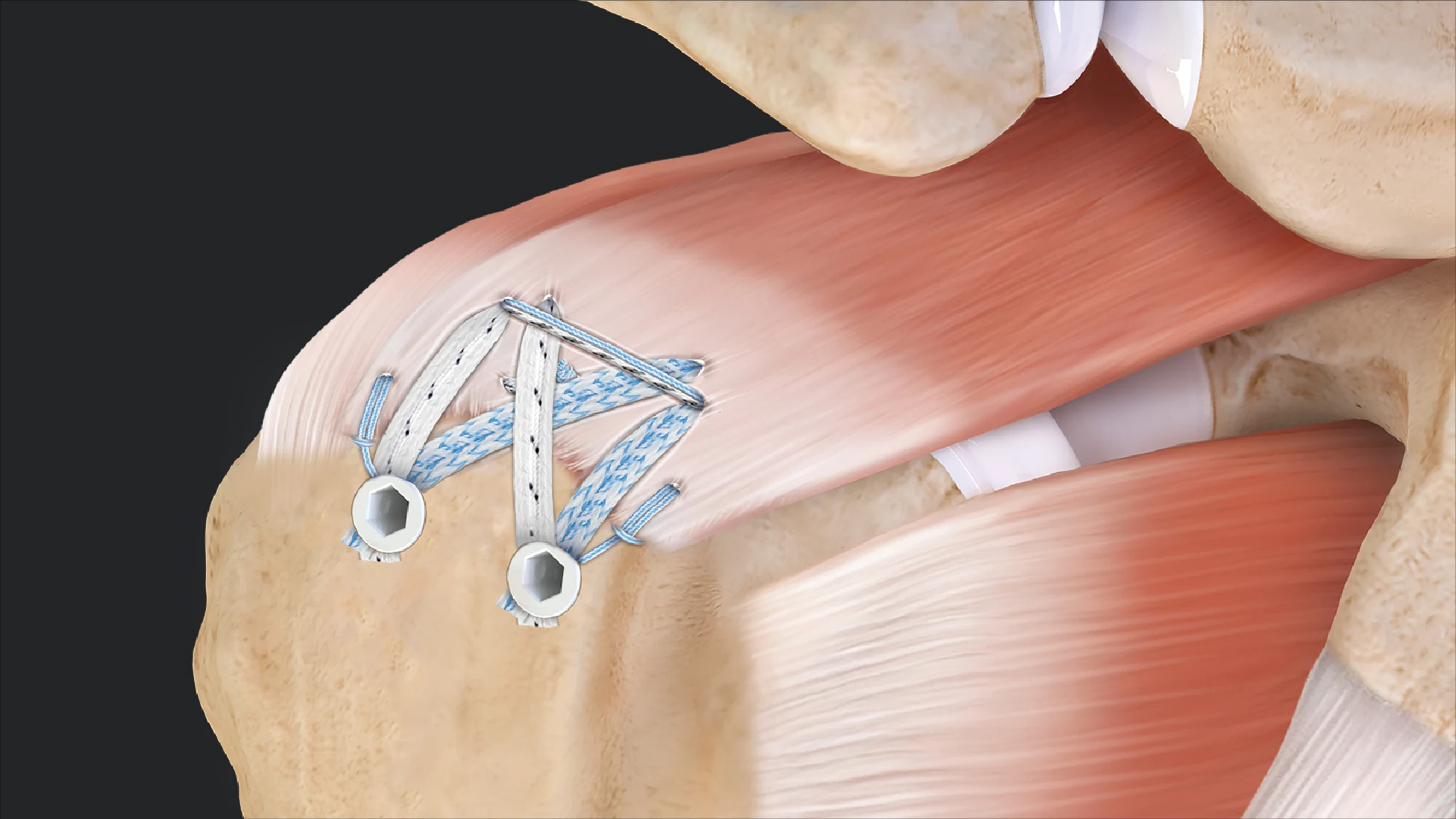
Treatment may include rest, ice, pain medications, physical therapy, corticosteroid injections, and in severe cases or for large tears, surgical repair to reattach the torn tendon to the bone.
What is the recovery time for a rotator cuff tear ?
Recovery time varies depending on the size and severity of the tear, as well as the individual’s age, overall health, and adherence to the treatment plan, but it can take several weeks to months to fully recover.
What are the potential complications of a rotator cuff tear ?
Complications may include chronic pain, weakness, stiffness, loss of shoulder function, and recurrent tears if the injury is not properly treated or if there is underlying degeneration of the tendon tissue.
Can a rotator cuff tear be prevented ?
While it may not be possible to prevent all rotator cuff tears, maintaining good shoulder strength and flexibility, using proper lifting techniques, avoiding repetitive overhead activities, and addressing shoulder pain or discomfort early can help reduce the risk.
When should I seek medical attention for a rotator cuff tear ?
You should seek medical attention if you experience persistent shoulder pain, weakness, or limited mobility that interferes with your daily activities or does not improve with rest and self-care measures, as prompt treatment can help prevent further damage and promote faster recovery.
