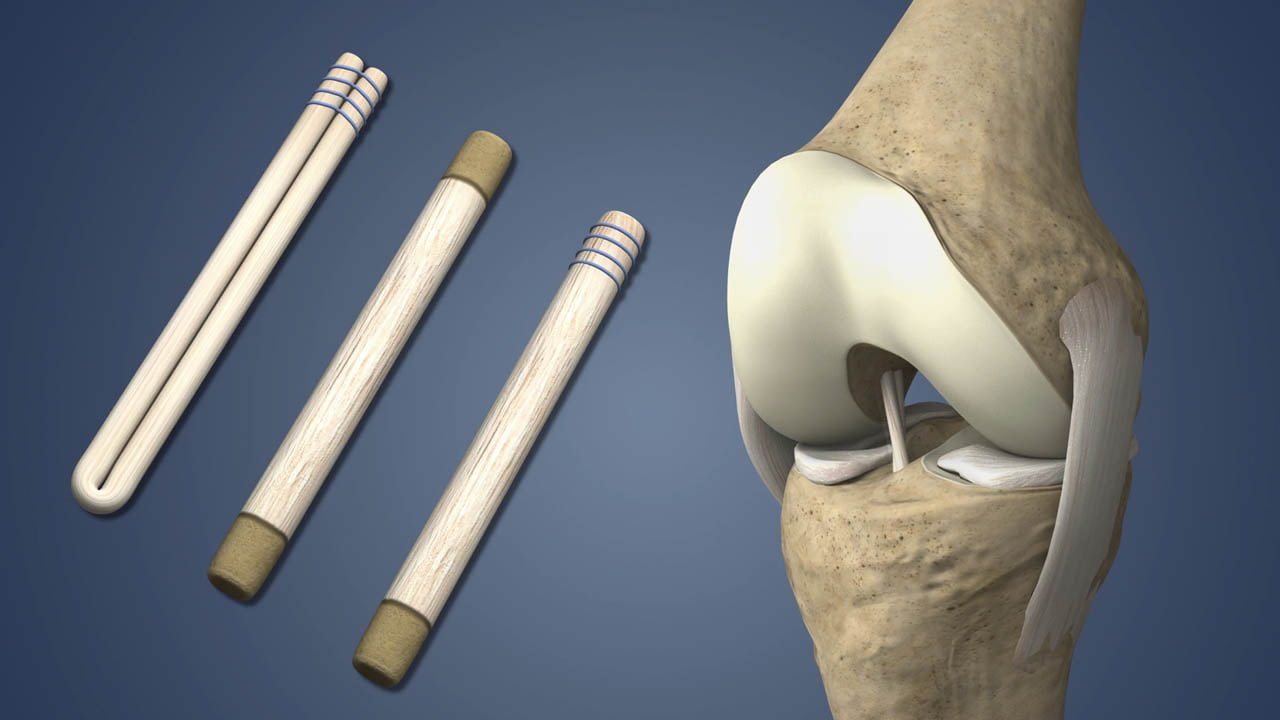
The surgical procedure typically involves repairing the torn ligament using sutures or replacing the damaged ligament with a graft. Grafts can be sourced from various locations, such as the patient’s own tissue (autograft) or from donor tissue (allograft). Commonly used grafts include the patellar tendon, hamstring tendon, or ligaments from cadaver donors.
Ligament Reconstruction
The surgery is often performed arthroscopically, using minimally invasive techniques with small incisions and specialized instruments. Arthroscopic surgery offers advantages such as shorter recovery times, reduced risk of complications, and less postoperative pain compared to traditional open surgery.
Rehabilitation following ligament reconstruction is crucial for successful outcomes. Physical therapy plays a significant role in restoring strength, flexibility, and range of motion to the joint. Patients typically undergo a structured rehabilitation program tailored to their specific needs and goals, gradually progressing from gentle exercises to more strenuous activities as the joint heals.
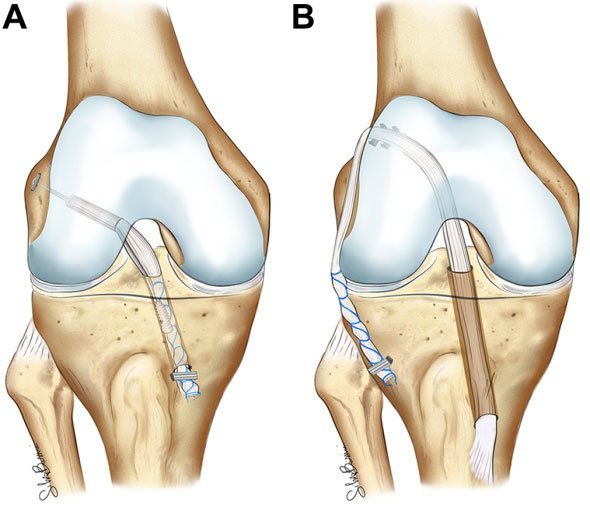
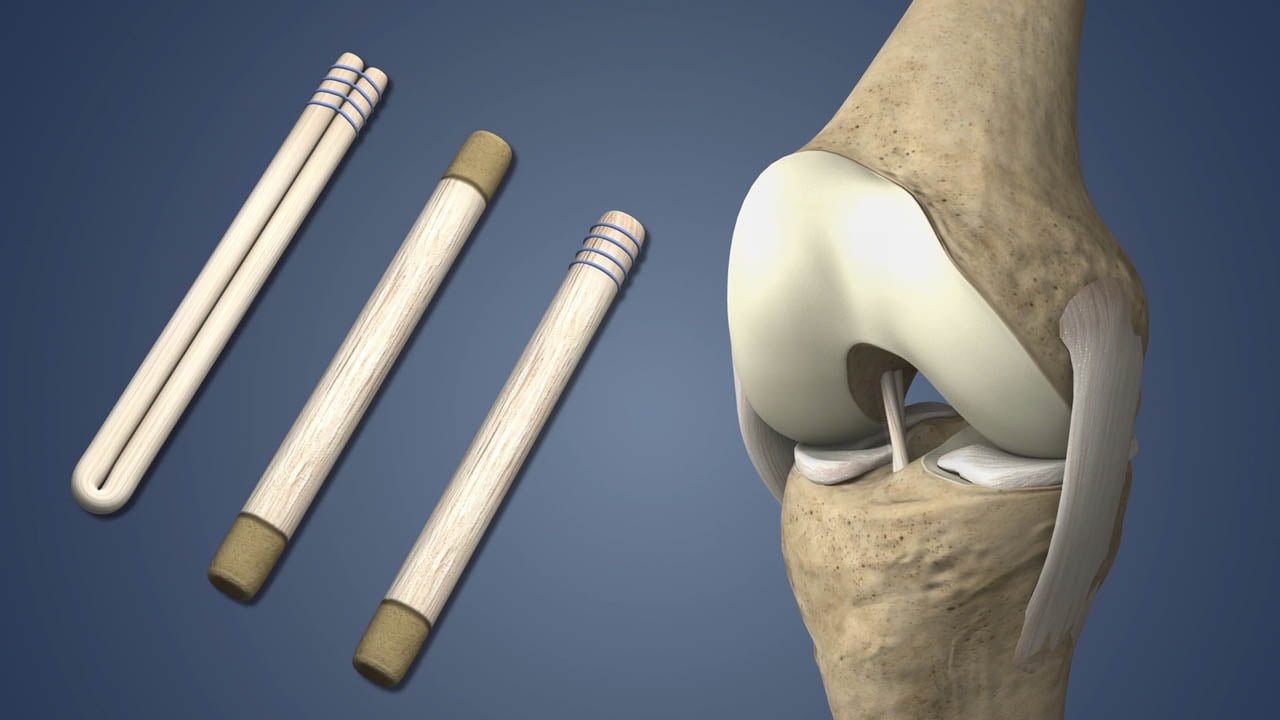
Ligament reconstruction is a surgical procedure performed to repair or reconstruct damaged ligaments in the body. Ligaments are tough bands of fibrous tissue that connect bones to other bones, providing stability and support to joints. When ligaments are injured or torn, it can lead to instability and pain in the affected joint.
Common reasons for ligament reconstruction surgery include:
- Ligament tears: Severe tears or complete ruptures of ligaments, often resulting from sports injuries or accidents, may require surgical intervention to restore stability to the joint.
- Chronic instability: Some individuals may experience recurrent dislocations or instability in a joint due to ligament laxity. Ligament reconstruction can help tighten and stabilize the joint to prevent further issues.
- Degenerative conditions: Conditions such as osteoarthritis or chronic ligamentous laxity may necessitate ligament reconstruction to alleviate pain and improve joint function.
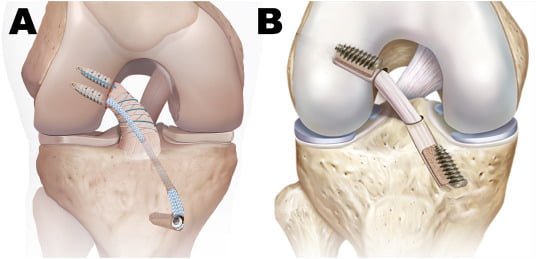
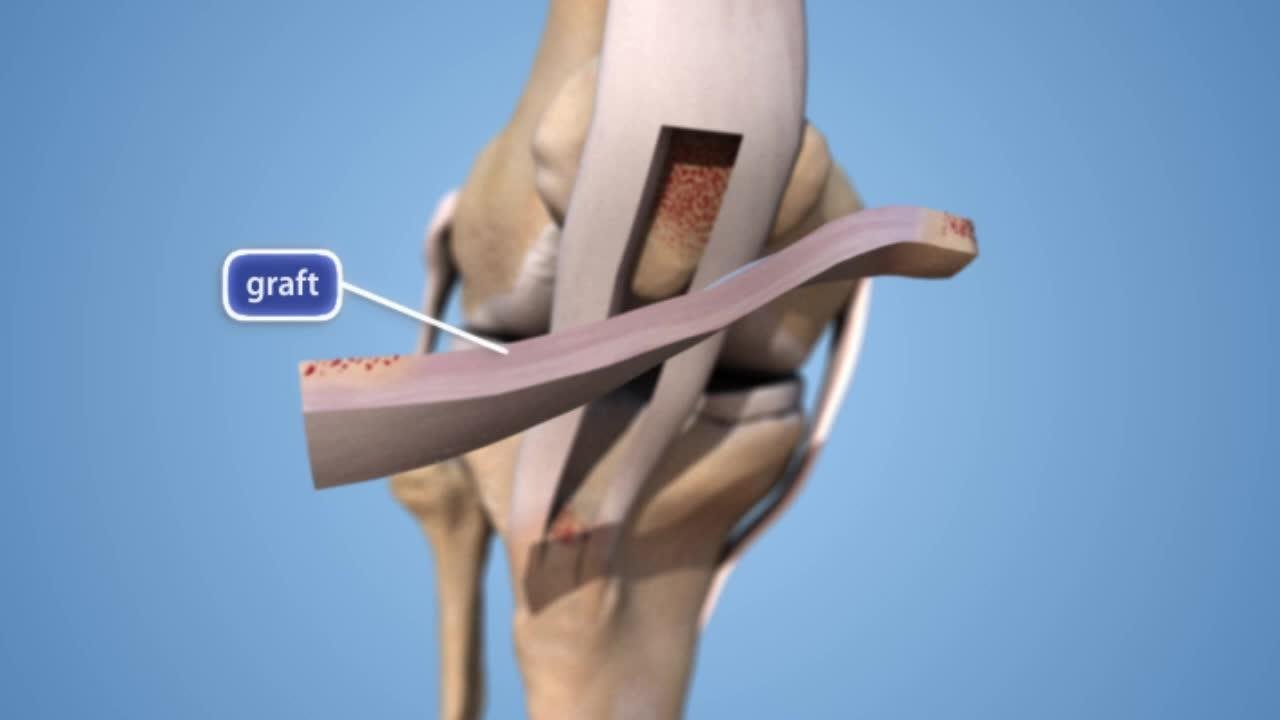
FAQ...
What is ligament reconstruction ?
Ligament reconstruction is a surgical procedure aimed at repairing or reconstructing damaged ligaments in the body, often in joints like the knee, ankle, or shoulder.
What are the common reasons for ligament reconstruction surgery ?
Ligament tears, chronic instability, and degenerative conditions such as osteoarthritis can necessitate ligament reconstruction surgery.
How is ligament reconstruction performed ?
The surgery typically involves repairing the torn ligament using sutures or replacing it with a graft, which can be sourced from the patient’s own tissue (autograft) or from a donor (allograft).
What are the advantages of arthroscopic ligament reconstruction ?
Arthroscopic surgery offers benefits such as smaller incisions, reduced risk of complications, shorter recovery times, and less postoperative pain compared to traditional open surgery.
What types of grafts are commonly used in ligament reconstruction ?
Commonly used grafts include the patellar tendon, hamstring tendon, or ligaments from cadaver donors.
How important is rehabilitation after ligament reconstruction surgery ?
Rehabilitation is crucial for successful outcomes, as it helps restore strength, flexibility, and range of motion to the joint.
What does the rehabilitation process involve ?
The rehabilitation process typically involves a structured program of exercises and physical therapy tailored to the patient’s specific needs and goals.
How long does it take to recover from ligament reconstruction surgery ?
Recovery times can vary depending on factors such as the type of surgery performed and individual healing rates, but it generally takes several months to fully recover.
What are the potential risks and complications associated with ligament reconstruction surgery ?
Risks and complications may include infection, blood clots, nerve damage, stiffness, and graft failure.
When can patients expect to return to sports or physical activities after ligament reconstruction surgery ?
Return to sports or physical activities typically occurs gradually, following clearance from the surgeon and completion of the rehabilitation program. It may take several months before patients can resume high-impact activities.
